Two things that are often not considered when it comes to acing maths are understanding maths history and developing a profound maths vocabulary.
In this article, where the focus is on increasing your maths vocabulary list, you will find advice and inspiration on how to do just that!
Want to give private lessons?
Join the Superprof community and share your knowledge with inquiring and motivated students.
Why Learn Maths Terms?
To succeed in mathematics, understanding the instructions, and using maths terms, is crucial. Although it may appear straightforward, there may be times when knowledge of essential math vocabulary will be absent. This could have disastrous effects on answering an exam question. To prevent encountering such obstacles, it is advisable to review maths terms and definitions before an exam.
Preparation like this will help you to understand and answer your exam questions and give you the confidence to tackle the problems presented.
In addition, growing your general maths vocabulary will help you to enjoy maths and thrive in it.
Superprof's Lexicon of Mathematical Terms
The following list of mathematical terms is worth printing out as it could help you to get over some of the blockages that tend to trip maths students up.
If you love maths or want to know why it is such an important and fascinating topic, why not read about the life of Albert Einstein and his contribution to mathematics?
Equation
An equation is defined as a mathematical statement that contains one or more variables.
The concept of an equation is fundamental to the maths vocabulary list for applying mathematics.
Factor
A factor is one of the maths terms involved in multiplication.
In the sum 3 x 24 = 72, 3 and 24 are the factors.

Product
As an example, take two numbers, namely a and b. The product of these numbers is the one that is obtained by multiplying a by b. This can also be represented as an x b.
Sum
A sum is the result of two terms being added together. If we consider, a and b as numbers, the sum represents number a that is added to b. This can also be represented as a + b.
Term
A "term" is when each element is involved in a sums relationship. For instance, this could be subtraction, addition, sequence, fraction or proportion.
For example: In the sequence 1, 2, 3, 4 the digits are terms. When represented as a ratio like 4/5, 4 and 5 are also terms.
Difference
In mathematics, "difference" is simply the result of a subtraction. For example, 4 - 3 = 1, so in this case, 1 is the difference.
Dividend
When two numbers or digits are divided, the dividend is the name given to the number being divided. For instance, in 36 ÷ 12, 36 will be the dividend.
Quotient
In mathematical terms, the word quotient refers to the result obtained from division. So, when 10 by 2 is divided, the quotient will be 5.
Numerator
The numerator is the first maths term used in a fraction. So, regarding the fraction 5/6, 5 will be the numerator.
Denominator
The denominator represents the second term in a fraction. So in the fraction 7/8, the 8 is the denominator and indicates how many equal parts the numerator (or unit) has been divided.
Triangle (isosceles, equilateral and rectangle)
A triangle is a polygon with three sides. An isosceles triangle is characterised by having two sides of equal length. A right-angled triangle, on the other hand, possesses an angle measuring 90°. The last of the math terms for a triangle is an equilateral triangle which is a type of triangle in which all three sides have the same length.
Are you familiar with some of the unexpected applications of mathematics? How about the misconceptions people have about maths?
Square
A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape characterised by four sides of equal length and four right angles (90°). Additionally, Greek mathematicians introduced another concept of a square: the square of a number. It refers to the result obtained by multiplying an integer by itself. For example, the square of 4, denoted as 42, equals 4 multiplied by 4, which equals 16.
Circle
A circle is a plane curve where every one of the points is equal from the centre point.
Rectangle
A rectangle is a parallelogram with two pairs of opposite sides that are parallel and four right angles measuring 90° each. It's worth noting that a square, satisfying both of these criteria, can also be classified as a rectangle.
Diamond
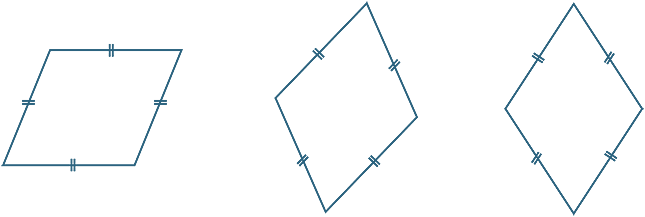
A diamond, or rhombus, is a parallelogram with all four sides of equal length (referred to as 'isometric'). It has parallel opposite sides and equal opposite angles. It also has diagonals that intersect at their midpoints, creating two axes of symmetry.
Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is simply a four-sided polygon.
Parallel
Parallel lines should have a constant distance from each other and they should not touch or intersect.
Perpendicular
When lines intersect at right angles, they are perpendicular to each other.
Segment
A segment is a piece of straight line bounded by two points, which are at each end of the segment. A segment [AB] (written in square brackets) has two points at their end, A and B. A segment can take the following forms:
- Circular e.g. a circle
- A curved segment which is limited by two points
- The section of a right angle, limited by 2 points.
- A section of a straight line.
Looking for math tutors near me? Let's tackle those tough equations together! Discover skilled tutors in your area who can simplify math concepts and help you excel. Whether it's exam prep, grade improvement, or just a confidence boost, our experienced tutors are here for you. Don't let math hold you back - start mastering it today!

Diagonal
In a polygon, a diagonal is a line segment that links two vertices that are not adjacent to each other. Consequently, a quadrilateral has a total of two diagonals.
Intersection
An intersection is a point at which two objects, whether geometric or groups meet.
Algebra
Algebra is a distinct branch of mathematics focused on manipulating and calculating the basic elements within a set of objects and its primary objective is to solve equations through explicit methods. Classical algebra encompasses the study of real numbers and complex numbers. Algebra defines the properties of operations and provides techniques for solving equations. Its applications extend beyond numbers to include geometry and complex numbers.
Whether you are looking for maths lessons online, or to upgrade your math vocabulary, Superprof has the solutions. why not find out how maths tutoring has evolved over the centuries?
Want to give private lessons?
Join the Superprof community and share your knowledge with inquiring and motivated students.
Geometry
Geometry is a distinct discipline within mathematics that encompasses the study of the relationships between points, curves, lines, and surfaces. It also includes the measurement of geometric figures and comprises various sub-branches, such as spatial geometry, planar geometry, geometric analysis, and projections. When you have an understanding of geometry it enables one to grasp the connections between:
Unknown
In an equation, an unknown refers to a missing term that needs to be determined. It represents the value that is yet to be found. For instance, in equation 5 + x = 8, the variable x (which is equal to 3) serves as the unknown term.
Coordinate
To determine the location of a point in two-dimensional space, a pair of numbers known as coordinates is required. These indicate the position in relation to both the horizontal line (abscissa) and the vertical line (ordinate).
Abscissa
The abscissa represents the perpendicular distance of a point from the vertical axis, and it is represented by a numerical value.
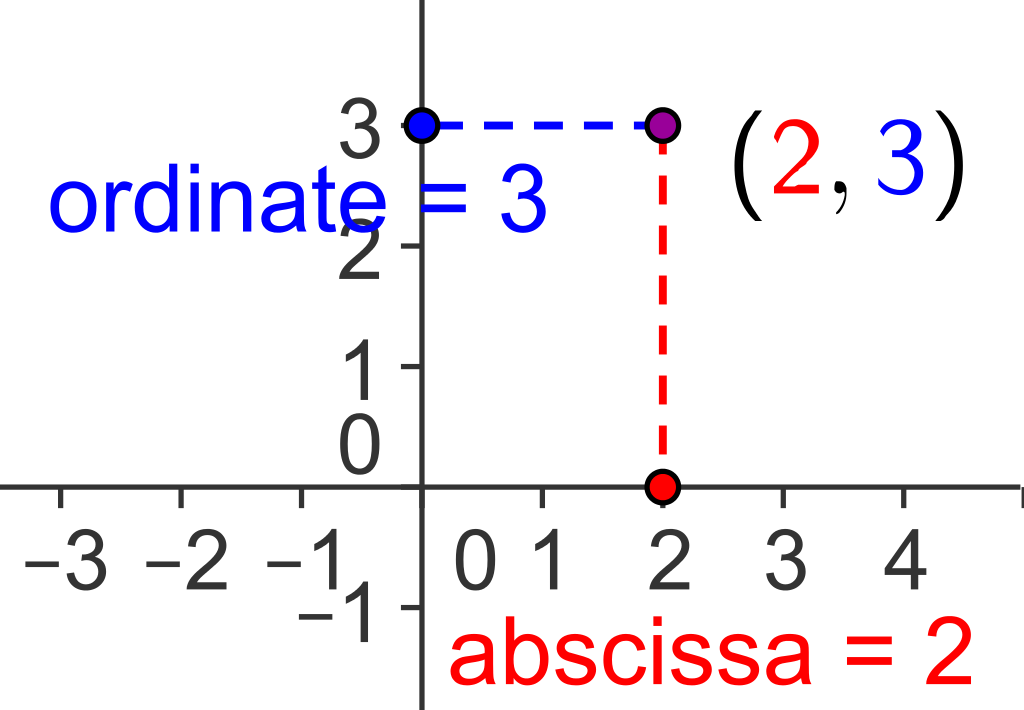
Ordinate
The ordinate represents the position relative to the horizontal axis, indicating the distance of a point from the vertical axis.
Ascending and descending order
In ascending order, numbers are arranged from the smallest to the largest. Conversely, in descending order, numbers are arranged from the largest to the smallest.
Angle
An angle is a geometric shape formed by two lines emanating from a common point. It is denoted by a small arc connecting the two lines near their point of origin.
Angles ranging from 0° to 90° are classified as acute, while angles between 90° and 180° are classified as obtuse. There are various other types of angles, including right angles (90°), zero angles (0°), flat angles (180°), and full angles (360°).
Hypotenuse
The hypotenuse is the side of a right-angled triangle that is opposite to the right angle.
Graph
A graph is a visual representation that showcases points or one or more lines, illustrating the changes in a measurable quantity.
Theorem
A theorem is a provable statement that emerges from previously established propositions. Pythagoras' theorem and Thales' theorem are notable examples that are widely recognised and referenced.
Did you know understanding things like math vocabulary or even the history of maths, could help you to make sense of your mathematics studies today?
Want to give private lessons?
Join the Superprof community and share your knowledge with inquiring and motivated students.
Summarise with AI:





